6 finish newton s laws and circular motion energy work definition examples of work work and kinetic energy conservative and non conservative forces work and potential energy conservation of energy.
Work energy theorem examples pdf.
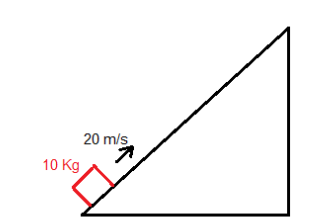
Therefore we first need to determine the car s kinetic energy at the moment of braking using.
Where w g work done by gravity.
W n work done by a normal.
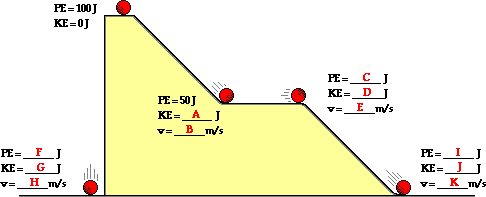
Friction or air resistance present then the system is not closed and the mechanical energy of the system will change.
Then we can state a very important physical principle.
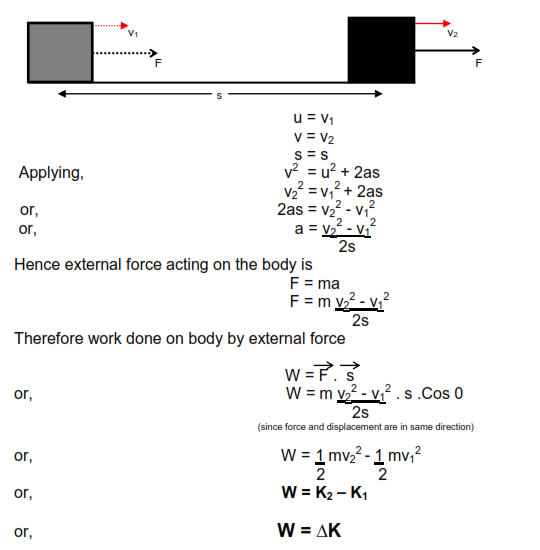
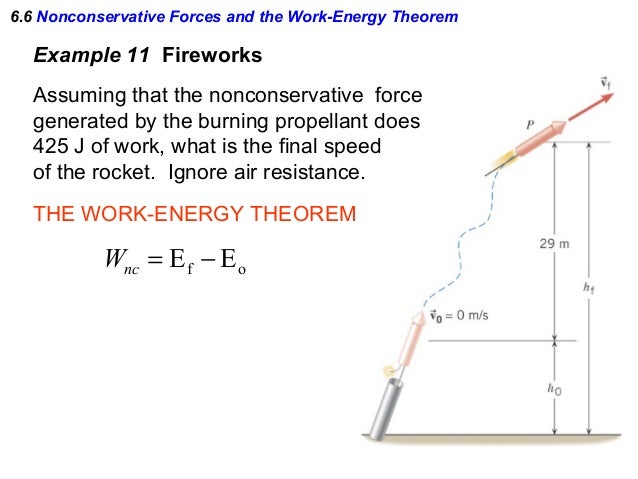
The work energy theorem states that the net work done on an object by the net force is equal to the change in kinetic energy of the object.
W g w n w f k f k i.
The work energy theorem explains the reasons behind this physics of no work.
Both kinetic energy and work are scalars.
K k f k i w in the above example with the ball falling from a.
We apply the work energy theorem.
Also here the work done is the work done by all forces acting on the body like gravity friction external force etc.
But physics itself might not agree on this.
Work energy and power tuesday february 10th reading.
1122 work 22 mv f mv 0.
The term work is used in everyday life quite frequently and we understand that it s an act of doing something.
Up to page 88 in the text book ch.
The work done is equal to the change in the kinetic energy.
The work done by a resultant force is equal to the change in kinetic energy that it produces.
We know that all the car s kinetic energy is lost to friction.
This definition can be extended to rigid bodies by defining the work of the torque and rotational kinetic energy.
Therefore the change in the car s kinetic energy is equal to the work done by the frictional force of the car s brakes.
For example you are working right now on your grasp of physics by reading this article.
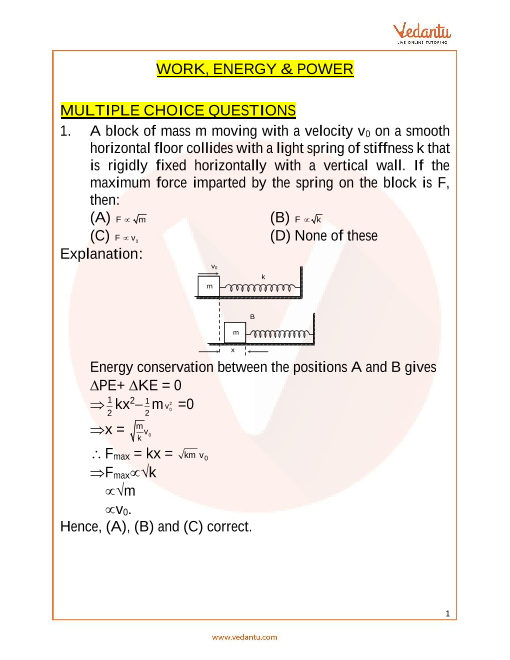
For example consider the following figure according to work energy theorem work done by all the forces change in kinetic energy.
The work energy theorem work is equal to the change in mv2 if we define kinetic energyas mv2then we.
The work energy theorem is useful however for solving problems in which the net work is done on a particle by external forces is easily computed and in which we are interested in finding the particles speed at certain positions of even more significance is the work energy theorem as a starting point for a broad generalization of the concept.